From Sensor to Cloud Networking in the Age of Digitalization by Phoenix Contact
Digitalization in industry is a prerequisite for making processes more flexible in order to remain economical and competitive in the future, even with increasing complexity. However, this requires an enormous amount of data. Also, directly from the process; of machines, systems, field devices, sensors and actuators. This is the only way to drastically optimize processes, for example with the help of predictive maintenance and self-optimizing processes (keywords: process analytics and big data analytics). The prerequisite for this is that everything can communicate with everything.
This requires a continuous and efficient network infrastructure:
- Ethernet up to the last meter: Smart devices,
- sensors and actuators are integrated into the Ethernet network
- mobile, flexible and area-wide communication is required
- all devices speak the same language
- real-time communication in the network is ensured
- data security becomes the standard for all communication
Today’s Ethernet connections and the supply of power to end devices often require too much space, power dissipation and are too expensive in relation to the device costs. A network connection is therefore often uneconomical. In order to be able to integrate the smart field devices economically and practically into the network, a low-cost, simple and space-saving connection technology is required for the network connection and the power supply. The solution: Single Pair Ethernet (SPE) & Advance Physical Layer (APL)
What exactly is Ethernet APL?
 The abbreviation APL stands for Advanced Physical Layer and describes a further development of physical data transmission in Ethernet networks. This physical layer makes it possible to exchange Ethernet data via only two wires, instead of the previously required four or eight wires.
The abbreviation APL stands for Advanced Physical Layer and describes a further development of physical data transmission in Ethernet networks. This physical layer makes it possible to exchange Ethernet data via only two wires, instead of the previously required four or eight wires.
Aside from pure communication, the technology also optionally enables the supply of power to be connected devices on the same pair of wires.
Ethernet APL therefore is one of several manifestations of the Single Pair Ethernet (SPE) and enables the direct connection of sensors, thereby making possible a continuous communication to the last few meters in the field.
The APL technology offers the following features:
- Bridging large distances: Trunk lengths of up to 1,000 m, spurs up to 200 m
- Use in explosion-protected areas is possible (zones 0, 1, and 2)
- Interoperability of the devices and systems of different manufacturers
- Capture and analysis of huge amounts of additional data is possible (big data) – new solutions such as predictive maintenance can be realized to increase availability
- Cost-efficient modernization of systems thanks to use of existing cabling and proven Ethernet protocols such as EtherNet/IP™, HART IP, OPC UA, and PROFINET
Mobile, flexible and area-wide communication is required
Today’s systems such as WLAN or 4G cannot meet these requirements because there is no exclusive transmission medium. This means that all communication takes place via a common medium or spectrum (frequency range), the availability of which is shared between the respective users. We also speak of a “shared medium”. Since the medium is shared between the users, there is no control over its availability and therefore no guarantee for the real-time capability of a system. You never know how many others you’ll share the medium with. The solution: 5G.
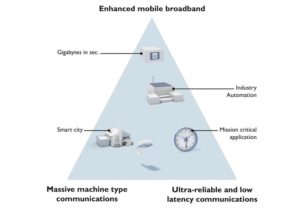 Depending on requirements, the new 5G mobile communications standard offers enormous bandwidth in the gigabit range, real-time capability or high subscriber numbers with extremely high reliability and security. In addition, private networks can be realized for the first time. Thus, 5G meets all requirements for a flexible and future-proof network connection in mobile or highly flexible applications.
Depending on requirements, the new 5G mobile communications standard offers enormous bandwidth in the gigabit range, real-time capability or high subscriber numbers with extremely high reliability and security. In addition, private networks can be realized for the first time. Thus, 5G meets all requirements for a flexible and future-proof network connection in mobile or highly flexible applications.
Conclusion: New communication standards such as OPC UA, TSN, SPE, and 5G are currently being created by various committees and in standardization projects. These new technologies, however, are not to be considered independent of each other – rather, they will form the communication of the future together.
As a technology leader with more than 30 years of experience in industrial communication technology, Phoenix Contact is actively involved in all of the key standardization committees. In these committees, we are helping to shape the new, cross-manufacturer communication standard for automation for you.
For further details
Please contact
Phoenix Contact India Pvt. Ltd.
F-26/2, Okhla Industrial Area
Phase -2, New Delhi – 110020
E-mail- adverts@phoenixcontact.co.in